CERTIFIED NETWORK DEFENDER
A Gateway to Cybersecurity Career
Follow a unique “PROTECT-DETECT-RESPONSE” Approach.

Target Audience
Network Administrators, Network Security Engineers, Network Security Analyst, Network Technicians, and Security Operators.
Course Details
Covers the protect, detect, and response approach network security. Contains hands-on labs based on major network security tools and techniques to provide network administrators with real-world expertise on security technologies and operations.
Certification
CND is a vendor-neutral, hands-on, instructor-led comprehensive network security certification program and prepares individuals on network security technologies and operations to achieve defense-in-depth objectives.
Complete Package USD $720
CERTIFIED NETWORK DEFENDER PROGRAM
Certified Network Defender (CND) is a vendor-neutral, hands-on, instructor-led comprehensive network security certification training program. It is a skills-based, lab intensive program based on a job-task analysis and cybersecurity education framework presented by the National Initiative of Cybersecurity Education (NICE). The course has also been mapped to global job roles and responsibilities and the Department of Defense (DoD) job roles for system/network administrators. The course is designed and developed after extensive market research and surveys.
The program prepares network administrators on network security technologies and operations to attain Defense-in-Depth network security preparedness. It covers the protect, detects, and respond approach to network security. It also teaches you network defense fundamentals, the application of network security controls, protocols, perimeter appliances, secure IDS, VPN, firewall configuration, intricacies of network traffic signature, analysis, and vulnerability scanning which will help you when you design greater network security policies and successful incident response plans. These skills will help you foster resiliency and continuity of operations during attacks. The course contains hands-on labs, based on major network security tools and techniques which will provide network administrators real-world expertise on current network security technologies and operations. The study-kit provides you with over 10 GB of network security best practices, assessments, and protection tools. The kit also contains templates for various network policies and a large number of white papers for additional learning.

The purpose of the CND credential is to:
Validate the skills that will help the Network Administrators foster resiliency and continuity of operations during attacks.
More about CND
The Certified Network Defender (CND) certification program focuses on creating Network Administrators who are trained on protecting, detecting, and responding to the threats on the network. Network administrators are usually familiar with network components, traffic, performance and utilization, network topology, location of each system, security policy, etc.
Network Administrators can become the first line of defense for the organization if they have enough security skills or are trained properly. A CND will get a fundamental understanding of the true construct of data transfer, network technologies, software technologies so that they understand how networks operate, understand what software is automating and how to analyze the subject material.
The Most Comprehensive Network Security Certification Course in the World
This is the world’s most advanced Certified Network Defense course with 14 of the most current network security domains any individuals will ever want to know when they are planning to protect, detect, and respond to the network attacks.
Why Certified Network Defender?
Organizational focus on cyber defense is more important than ever as cyber breaches have a far greater financial impact and can cause broad reputational damage. Despite the best efforts to prevent breaches, many organizations are still being compromised. Therefore organizations must have, as part of their defense mechanisms, trained network engineers who are focused on protecting, detecting, and responding to the threats on their networks.
Network administrators spend a lot of time with network environments and are familiar with network components, traffic, performance and utilization, network topology, location of each system, security policy, etc. So, organizations can be much better in defending themselves from vicious attacks if the IT and network administrators equipped with adequate network security skills. Thus Network administrators can play a significant role in network defense and become the first line of defense for any organization.
COMPONENTS OF CND FOCUS
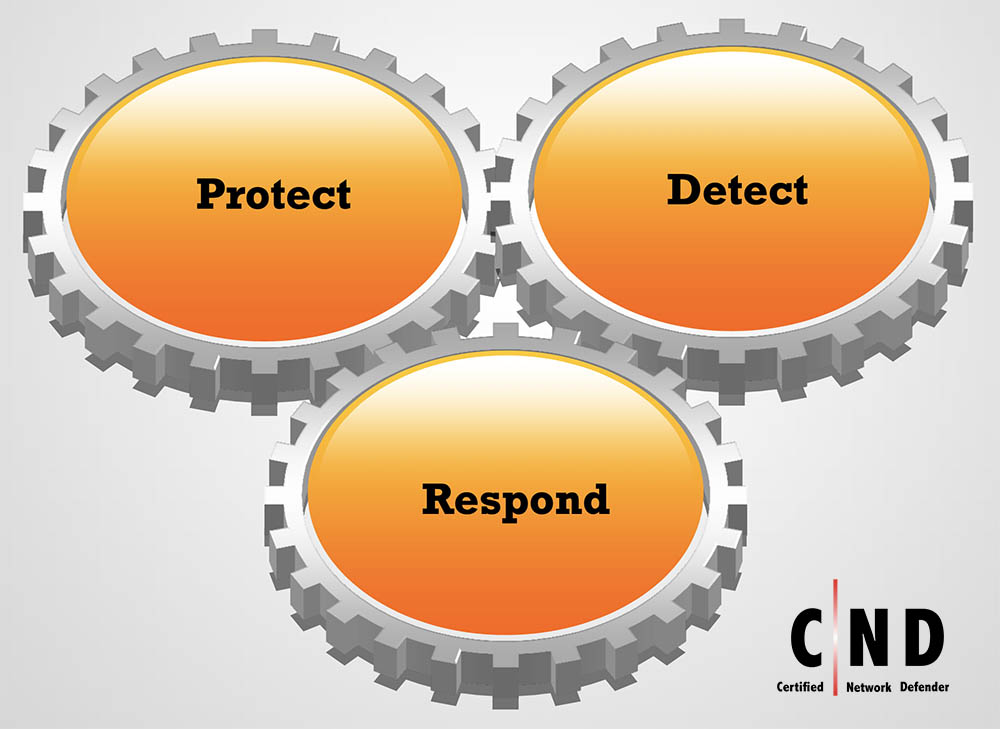
PROTECT
Refers to the implementation of controls to achieve Defense-in-Depth protection”
Policies ● Physical Security ● Host Security ● Firewalls ● IDS/IPS
DETECT
Refers to development and use of processes, techniques, and tools to detect security bypass attempts; it guides you through the detection of incidents
Network Monitors ● Log Management ● Vulnerability Scanning ● Risk Management
RESPOND
If an incident does occur, CND guides you through the incident response process and post-incident actions to contain the damage.
Incident Handling● Incident Response ● Data Back and Recovery

CND Course Outline
THE ULTIMATE CERTIFICATION FOR NETWORK ADMINISTRATORS
Network Fundamentals
Network Components
TCP/IP Networking Basics
TCP/IP Protocol Stack
IP Addressing
Computer Network Defense (CND)
CND Triad
CND Process
CND Actions
CND Approaches
Essential Terminologies
Network Security Concerns
Network Security Vulnerabilities
Network Reconnaissance Attacks
Network Access Attacks
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Distributed Denial-of-Service Attack (DDoS)
Malware Attacks
Fundamental Elements of Network Security
Network Security Controls
User Identification, Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
Types of Authorization Systems
Authorization Principles
Cryptography
Security Policy
Network Security Devices
Network Security Protocols
What is Security Policy?
Internet Access Policies
Acceptable-Use Policy
User-Account Policy
Remote-Access Policy
Information-Protection Policy
Firewall-Management Policy
Special-Access Policy
Network-Connection Policy
Business-Partner Policy
Email Security Policy
Passwords Policy
Physical Security Policy
Information System Security Policy
Bring Your Own Devices (BYOD) Policy
Software/Application Security Policy
Data Backup Policy
Confidential Data Policy
Data Classification Policy
Internet Usage Policies
Server Policy
Wireless Network Policy
Incidence Response Plan (IRP)
User Access Control Policy
Switch Security Policy
Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDS/IPS) Policy
Personal Device Usage Policy
Encryption Policy
Router Policy
Security Policy Training and Awareness
ISO Information Security Standards
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS)
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Information Security Acts: Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX)
Information Security Acts: Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA)
Information Security Acts: The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) and Federal
Information Security Management Act (FISMA)
Other Information Security Acts and Laws
Physical Security
Access Control Authentication Techniques
Physical Security Controls
Other Physical Security Measures
Workplace Security
Personnel Security: Managing Staff Hiring and Leaving Process
Laptop Security Tool: EXOS
Environmental Controls
Physical Security: Awareness /Training
Physical Security Checklists
Host Security
OS Security
Linux Security
Securing Network Servers
Hardening Routers and Switches
Application/Software Security
Data Security
Virtualization Security
Firewalls and Concerns
What Firewalls Does?
What should you not Ignore?: Firewall Limitations
How Does a Firewall Work?
Firewall Rules
Types of Firewalls
Firewall Technologies
Firewall Topologies
Firewall Rule Set and Policies
Firewall Implementation
Firewall Administration
Firewall Logging and Auditing
Firewall Anti-evasion Techniques
Why Firewalls are Bypassed?
Full Data Traffic Normalization
Data Stream-based Inspection
Vulnerability-based Detection and Blocking
Firewall Security Recommendations and Best Practices
Firewall Security Auditing Tools
Intrusions and IDPS (Intrusion, Detection and Prevention Systems)
Types of IDS Implementation
IDS Deployment Strategies
Types of IDS Alerts
IDPS Product Selection Considerations
IDS Counterparts
Understanding Virtual Private Network (VPN)
How VPN works?
Why Establish a VPN ?
VPN Components
VPN Concentrators
Types of VPN
VPN Categories
Selecting Appropriate VPN
VPN Core Functions
VPN Technologies
VPN Topologies
Common VPN Flaw
VPN Security
Quality Of Service and Performance in VPNs
Wireless Terminologies
Wireless Networks
Wireless Standard
Wireless Topologies
Typical Use of Wireless Networks
Components of Wireless Network
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Encryption
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) Encryption
WPA2 Encryption
WEP vs. WPA vs. WPA2
Wi-Fi Authentication Method
Wi-Fi Authentication Process Using a Centralized Authentication Server
Wireless Network Threats
Bluetooth Threats
Wireless Network Security
Wi-Fi Discovery Tools
Locating Rogue Access points
Protecting from Denial-of-Service Attacks: Interference
Assessing Wireless Network Security
Wi-Fi Security Auditing Tool: AirMagnet WiFi Analyzer
WPA Security Assessment Tool
Wi-Fi Vulnerability Scanning Tools
Deploying Wireless IDS (WIDS) and Wireless IPS (WIPS)
WIPS Tool
Configuring Security on Wireless Routers
Additional Wireless Network Security Guidelines
Network Traffic Monitoring and Analysis(Introduction)
Network Monitoring: Positioning your Machine at an Appropriate Location
Network Traffic Signatures
Packet Sniffer: Wireshark
Detecting OS Fingerprinting Attempts
Detecting PING Sweep Attempt
Detecting ARP Sweep/ ARP Scan Attempt
Detecting TCP Scan Attempt
Detecting SYN/FIN DDOS Attempt
Detecting UDP Scan Attempt
Detecting Password Cracking Attempts
Detecting FTP Password Cracking Attempts
Detecting Sniffing (MITM) Attempts
Detecting the Mac Flooding Attempt
Detecting the ARP Poisoning Attempt
Additional Packet Sniffing Tools
Network Monitoring and Analysis
Bandwidth Monitoring
What is Risk?
Risk Levels
Risk Matrix
Key Risk Indicators(KRI)
Risk Management Phase
Enterprise Network Risk Management
Vulnerability Management
Introduction to Data Backup
RAID (Redundant Array Of Independent Disks) Technology
Storage Area Network (SAN)
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
Selecting Appropriate Backup Method
Choosing the Right Location for Backup
Backup Types
Conducting Recovery Drill Test
Data Recovery
Windows Data Recovery Tool
RAID Data Recovery Services
SAN Data Recovery Software
NAS Data Recovery Services
Incident Handling and Response
Incident Response Team Members: Roles and Responsibilities
First Responder
Incident Handling and Response Process
Overview of IH&R Process Flow
What will you learn?
-
Students will learn about various network security controls, protocols, and devices
-
Students will able to troubleshoot their network for various network problems
-
Students will able to identify various threats on the organization network
-
Students will learn how to design and implement various security policies for their organizations
-
Students will learn the importance of physical security and able to determine and implement various physical security controls for their organizations
-
Students will able to harden the security of various hosts individually in the organization’s network
-
Students will able to choose appropriate firewall solution, topology, and configurations to harden security through firewall

-
Students will able to determine the appropriate location for IDS/IPS sensors, tuning IDS for false positives and false negatives, and configurations to harden security through IDPS technologies
-
Students will able to implement secure VPN implementation for their organization.
- Students will able to identify various threats to wireless networks and learn how to mitigate them.
- Students will able to monitor and conduct signature analysis to detect various types of attacks and policy violation activities.
- Students will able to perform risk assessment, vulnerability assessment/scanning through various scanning tools and generate detailed reports on it
-
Students will able to identify the critical data, choose an appropriate backup method, media, and technique to perform a successful backup of organization data.
-
Students will able to provide the first response to the network security incident and assist the IRT team and forensics investigation team in dealing with an incident.
What Does the CND Program Cover?
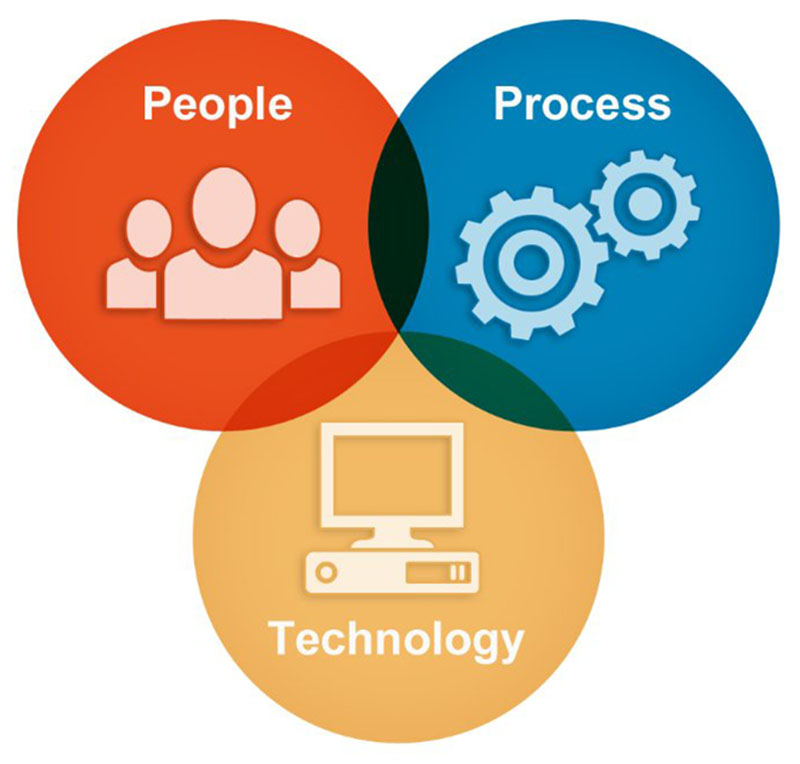
People
- Network Administrator
- Network Security Administrator
- Network Security Engineer
- Security Architects
- Security Analysts
- Network Technicians
- End Users
Process
- Creating and enforcing security policies
- Creating and enforcing standard network operating procedures
- Planning business continuity
- Configuration control management
- Creating and implementing incident response processes
- Planning data recovery
- Conducting forensics activities on incidents
- Providing security awareness and training
- Enforcing security as a culture
Technology
- Physical security
- Firewalls /IDS implementation
- OS hardening/patching
- Antivirus protection
- Encryption mechanism
- Authentication mechanism
- Configuration management
- Access control mechanism
- Proxy servers
- Packet/content filtering
- Product evaluation based on common criteria
- Passwords security
- Network logs audit
Why Network Administrators are So Important for an Organization?
Network administrators spend a lot of time with network environments and are familiar with network traffic, performance and utilization, network topology, location of each system, security policy, etc. If they provide protection, detection, and response to incidents in the early stages, organizations can contain or minimize the potential impact of an incident.
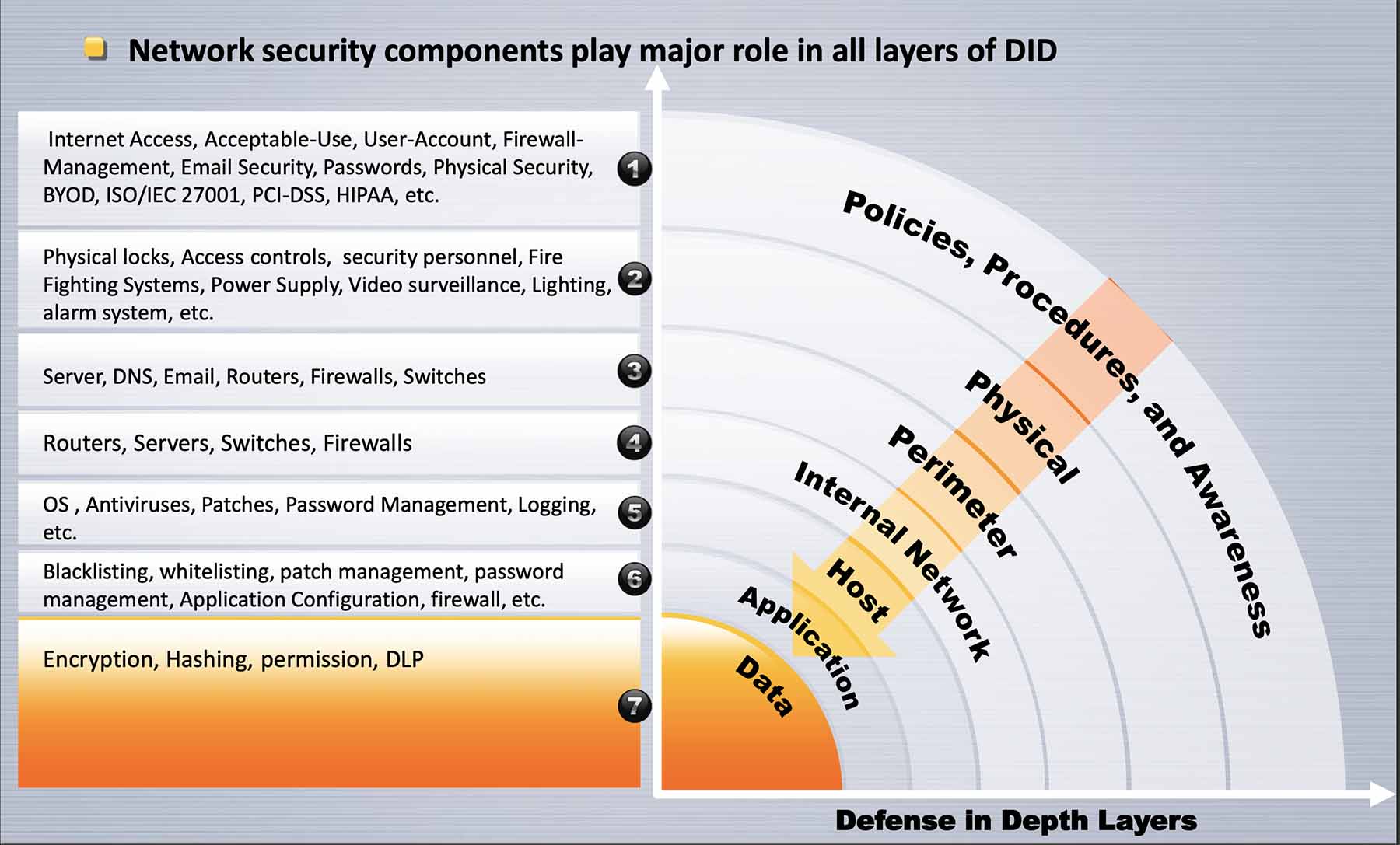
Network Security is a Major Component of Information Security Defense-in-Depth
CND Exams Information
Prove Your Skills and Abilities With Online, Practical Examinations.
Exam Title: Certified Network Defender (CND)
Exam Code: 312-38
# Questions: 100
Duration: 4 Hours
Test Format: Interactive Multi Choice Questions (MCQ)
Availability: ECC Exam Portal
Students should have a fundamental knowledge of networking concepts.
Personal
USD $720 / iLearn Kits
- 1 Year Full Access on Video Training
- 6 Months Access to iLab Machines
- 1 Year Access on Book, Slides, and Materials
- 24x7x365 support
- Exam Voucher Included
- Certificate of Attendance
- 1-hour Free Consultation
- 5% OFF on 3+ Kits
Groups Purchases
Starts from ANY 5 iLearn Kits
- All Personal Package
- The best option for Institutions, Universities, Companies, Organizations, and Startups
- 7% OFF on 5+ Kits
- 10% OFF on 10+ Kits
- 12% OFF on 15+ Kits
- 15% OFF on 20+ Kits
- 25+ Kits Contact us
iLearn Kits
Additional Promotion
- CLICK+ Members get 5% OFF on All Kits
- Students will get 5% OFF on All Kits
- Instructors will get 5% OFF on All Kits
- Offers can NOT be transferred to 3rd party
- Max 2 Offers will be applied to Purchases
We provide Training and Certification for all levels
* All Prices are in USD including:
- One Year Access Training Videos
- 6 Month Access iLab and Scenario
- Certificate Exam Voucher
- Certificate of Attendance
- Online Exam
- Books, Slides and Course Material
- 24X7X365 Support
Core
Security Principal and Cyber Awareness
- CND – Certified Network Defender $720
- CSCU – Certified Secure Computer User $130
- ECES – EC-Council Certified Encryption Specialist $400
- ECSS – EC-Council Certified Security Specialist $400
Advanced
Hands-On Experience on Cybersecurity
- CEH – Certified Ethical Hacker $720
- CEH Practical $200
- APT – Advanced Penetration Testing $400
- LPT – Licensed Penetration Tester $999
- CSA – Certified SOC Analyst $400
- ECSA – EC-Council Certified Security Analyst $720
- ECSA Practical $250
- CPM – Certified Project Management $270
Expert
Need more? Don’t worry, we’re here.
- CHFI – Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator $720
- ECIH – EC-Council Certified Incident Handler $400
- CTIA – Certified Threat Intelligence Analyst $400
- EDRP – EC-Council Disaster Recovery Professional $720
- CBP – Certified Blockchain Professional $720
- CASE .NET Certified Application Security Engineer $390
- CASE JAVA Certified Application Security Engineer $390
- CCISO – Certified Chief Information Security Officer $830
Frame your Future with CLICK+
EC-Council iLearn solution helps you to get trained with the latest techniques and skills in Cybersecurity domains. Click Plus professional team members always proud to help you find the best pathway of your training to promote your future. Wherever you are in your career, we are here to help!


